Netlify setup guide
Setup guide for configuring Turso using environment variables in an application deployed to Netlify.

In this setup guide, you will deploy a web application that uses Turso as its database. The deployment is configured with environment variables whose values are obtained from the Turso CLI.
You can find the source code for the app on GitHub.
#Prerequisites
- A Netlify account
- The Turso CLI installed on your machine (installation instructions)
#1. Set up the Turso database
#1a. Create a new database
Run the following CLI command:
$ turso db create findmeon
#1b. Access the database using the shell
Run the following CLI command:
$ turso db shell findmeon
#1c. Define and populate the database
Copy and paste the following SQL statements into the shell to create tables, indexes, and sample data:
-- users table
create table users(
id integer primary key,
email varchar(255) not null,
full_name varchar(100) not null,
username varchar(50) not null,
created_at integer default (cast(unixepoch() as int))
);
-- links table
create table links(
id integer primary key,
user_id integer not null,
website varchar(100) not null,
link text not null,
created_at integer default (cast(unixepoch() as int)),
foreign key(user_id) references users(id)
);
-- unique index for the email row
create unique index idx_users_email on users(email);
-- unique index for the username row
create unique index idx_users_username on users(username);
-- a multicolumn index for the user_id and link columns
create unique index idx_links_userid_link on links(user_id, link);
-- create user: "turso"
insert into users(id, email, full_name, username) values(1, "no-reply@turso.tech", "Turso", "turso");
-- add some links to "turso"
insert into links(user_id, website, link) values(1, "Twitter", "https://twitter.com/tursodatabase"),
(1, "Linkedin", "https://www.linkedin.com/company/turso/"),
(1, "GitHub", "https://github.com/chiselstrike/");
#1d. Quit the shell
Type the following at the shell prompt to terminate the shell:
.quit
#2. Deploy the app to Netlify
#2a. Start a guided installation
Click this button to start a guided deployment. It will automatically copy the app's source code into your personal GitHub and deploy it from there.
Note:
If you would prefer to fork and deploy the source repo and configure the deployment manually, follow the manual installation instructions at the end. The following instructions assume that you're using the above button to perform the deployment.
#2b. Connect your Netlify account to your GitHub account
Netlify will prompt you to log in with your GitHub account:

#2c. Provide values for the project's environment variables
The app (FindMeOn) requires two environment variables to enable it to connect to the database you created earlier: VITE_TURSO_DB_URL and VITE_TURSO_DB_AUTH_TOKEN. These values are required by the libSQL TypeScript client SDK to initialize the client and connect to the Turso database.
Netlify prompts you for those values on the page you see after logging in.
#Get the value for VITE_TURSO_DB_URL
Run the following CLI command:
$ turso db show findmeon --url
It outputs the URL for the database. Copy that string into the VITE_TURSO_DB_URL variable.
#Get the value for VITE_TURSO_DB_AUTH_TOKEN
Run the following CLI command:
$ turso db tokens create findmeon
This creates a long-lived authentication token that allows the libSQL client library used by the app to connect to the database.
Copy the string into the VITE_TURSO_DB_AUTH_TOKEN variable.
#Deploy the app
Click the "Save & Deploy" button to finalize the project's deployment.

This will take you to the "Site overview" page on your Netlify dashboard which displays the deployment status of the project. Once deployment is complete, you can verify that the app works.
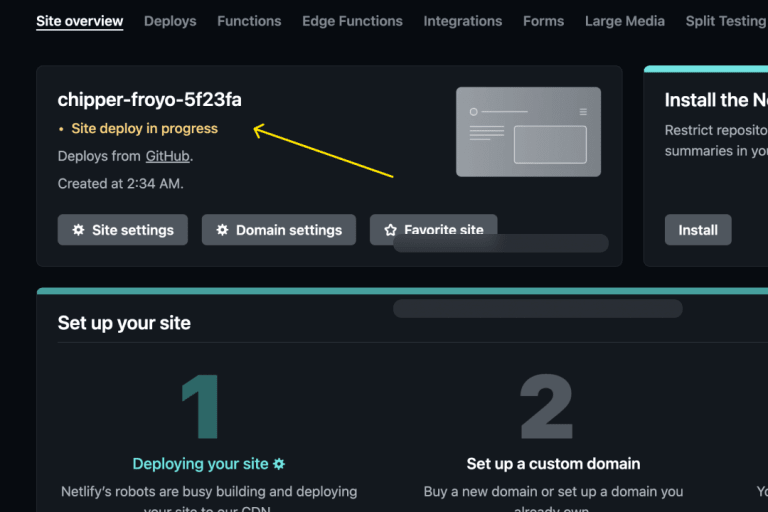
#3. Verify the app works
In step 1, you created and populated the database with some sample data. You can use the deployed app to view the sample data to verify that it's correctly connected to Turso.
Using the deployment URL provided by Netlify, visit the path /u/turso under it. This page displays the user data from the users and links tables.

#(Alternative) manual installation
If you want to deploy an app without the help of the "Deploy to Netlify" button in step 2, you can instead use the Netlify dashboard to manually specify your GitHub repo and configure its environment variables. The steps below walk you through this process using the same source repository.
#1. Fork the repo
Visit the project on GitHub and fork the repository to your own personal account.
#2. Import the project in the Netlify dashboard
Open your Netlify dashboard, add a new site, and import the existing project that you just forked.

#3. Connect to a Git provider
Choose GitHub from the list (if you forked the repo in step 1).

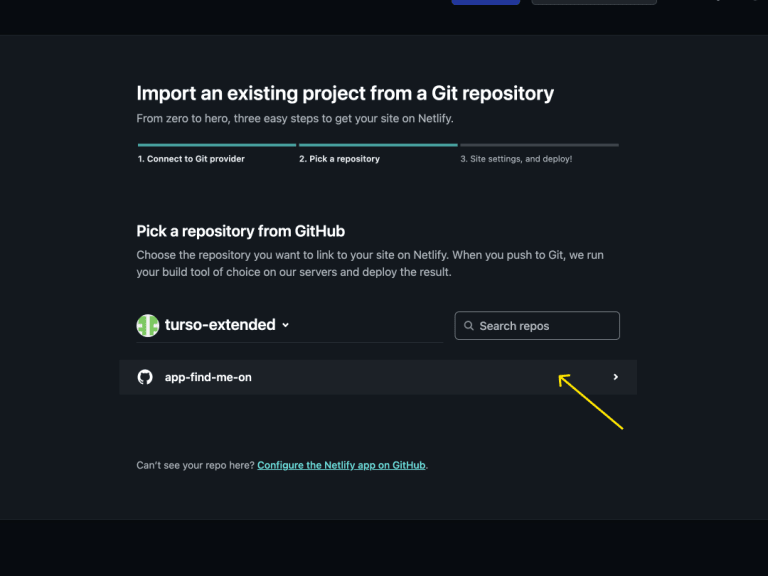
#4. Pick your project's repository
Netlify provides a list of repositories in your account. Choose your fork from the list.
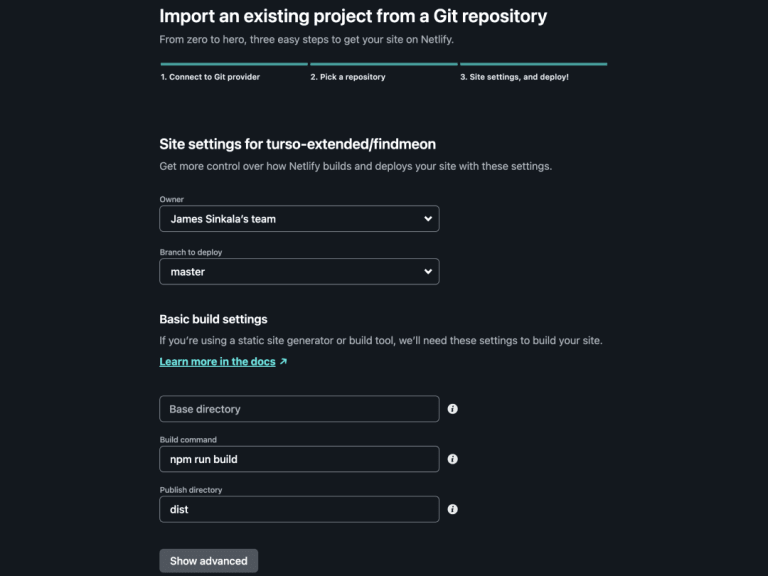
#5. Configure site settings
Configure the site settings for your project, including the production branch, build command, publish and base directory. (For most frameworks, Netlify automatically detects and sets this configuration.)
#6. Configure the app's environment variables
The app (FindMeOn) requires two environment variables to enable it to connect to the database you created earlier: VITE_TURSO_DB_URL and VITE_TURSO_DB_AUTH_TOKEN. These values are required by the libSQL TypeScript client SDK to initialize the client and connect to the Turso database.
Click the "Show advanced" button on the site setting page.
#6a. Create an environment variable for VITE_TURSO_DB_URL
Use the "New variable" button to create a new environment variable called VITE_TURSO_DB_URL.

Run the following CLI command:
$ turso db show findmeon --url
It outputs the URL for the database. Copy that string into the VITE_TURSO_DB_URL variable.
#6b. Create an environment variable for VITE_TURSO_DB_AUTH_TOKEN
Use the "New variable" button to create a new environment variable called VITE_TURSO_DB_AUTH_TOKEN.
Run the following CLI command:
$ turso db tokens create findmeon -e none
This creates a long-lived authentication token that allows the libSQL client library used by the app to connect to the database. The -e flag in this command is short for --expiration.
Copy the string into the VITE_TURSO_DB_AUTH_TOKEN variable.
#7. Deploy the site

#8. Preview the site after deployment
